Developing human heart data¶
Here we use a developing human heart dataset (Ji et al., Cell, 2020) to demonstrate the advanced usage of STRIDE. The original study provided 4, 9 and 6 heart sections from three timepoints, 4.5-6, 6.5, and 9 PCW, respectively, which were profiled by ST technology. They also provided a single-cell transcriptional profile of the 6.5 PCW tissue sample, generated through 10X Genomics Chromium platform. Users can download the processed data from here.
Step 1 Deconvolve the cell-type composition of ST data¶
Here we use the 6.5 PCW scRNA-seq data as a reference to deconvolve ST data of different timepoints. In this example, the scRNA-seq and the merged ST count matrices are stored in 10X HDF5 format. We also provide a custom marker gene list for STRIDE to achieve a better performance in distinguishing similar cell types. With all data prepared, we use STRIDE deconvolve to dicpher the cell-type compositions of ST data.
STRIDE deconvolve --sc-count Data/Human_heart_scRNA_gene_count.h5 \
--sc-celltype Data/Human_heart_scRNA_celltype_curated.txt \
--gene-use Data/Human_heart_scRNA_markers.txt \
--st-count Data/Human_heart_ST_gene_count.h5 \
--outdir Result/STRIDE --outprefix Human_heart --normalize
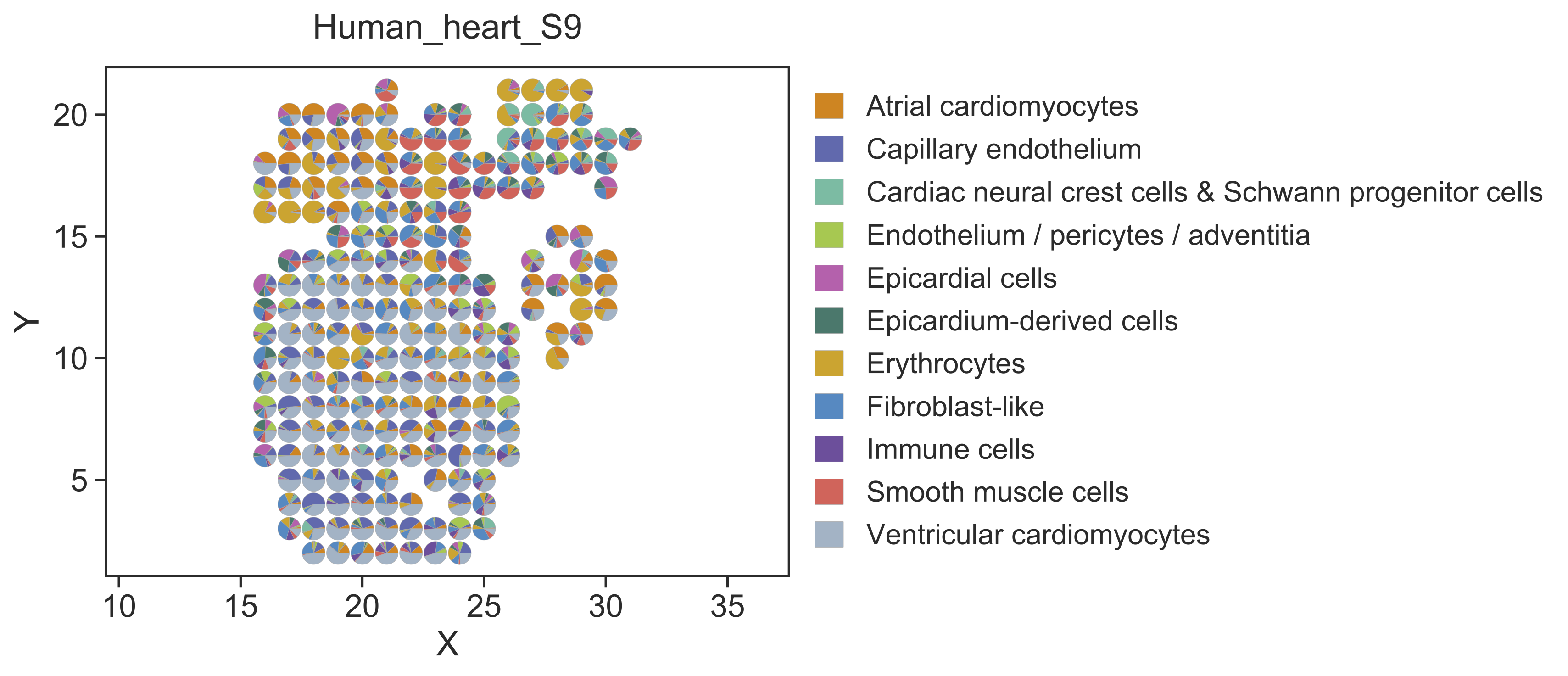
Step 2 Visualize the deconvolution result¶
After cell type deconvolution, STRIDE plot could be used to visualize the deconvolution result. Users can specify the sample of interest by setting --sample-id. Here we use sample 9 as an example.
STRIDE plot --deconv-file Result/STRIDE/Human_heart_spot_celltype_frac.txt \
--st-loc Data/Human_heart_ST_location.txt --sample-id 9 \
--plot-type scatterpie --pt-size 12 \
--outdir Result/STRIDE --outprefix Human_heart_S9
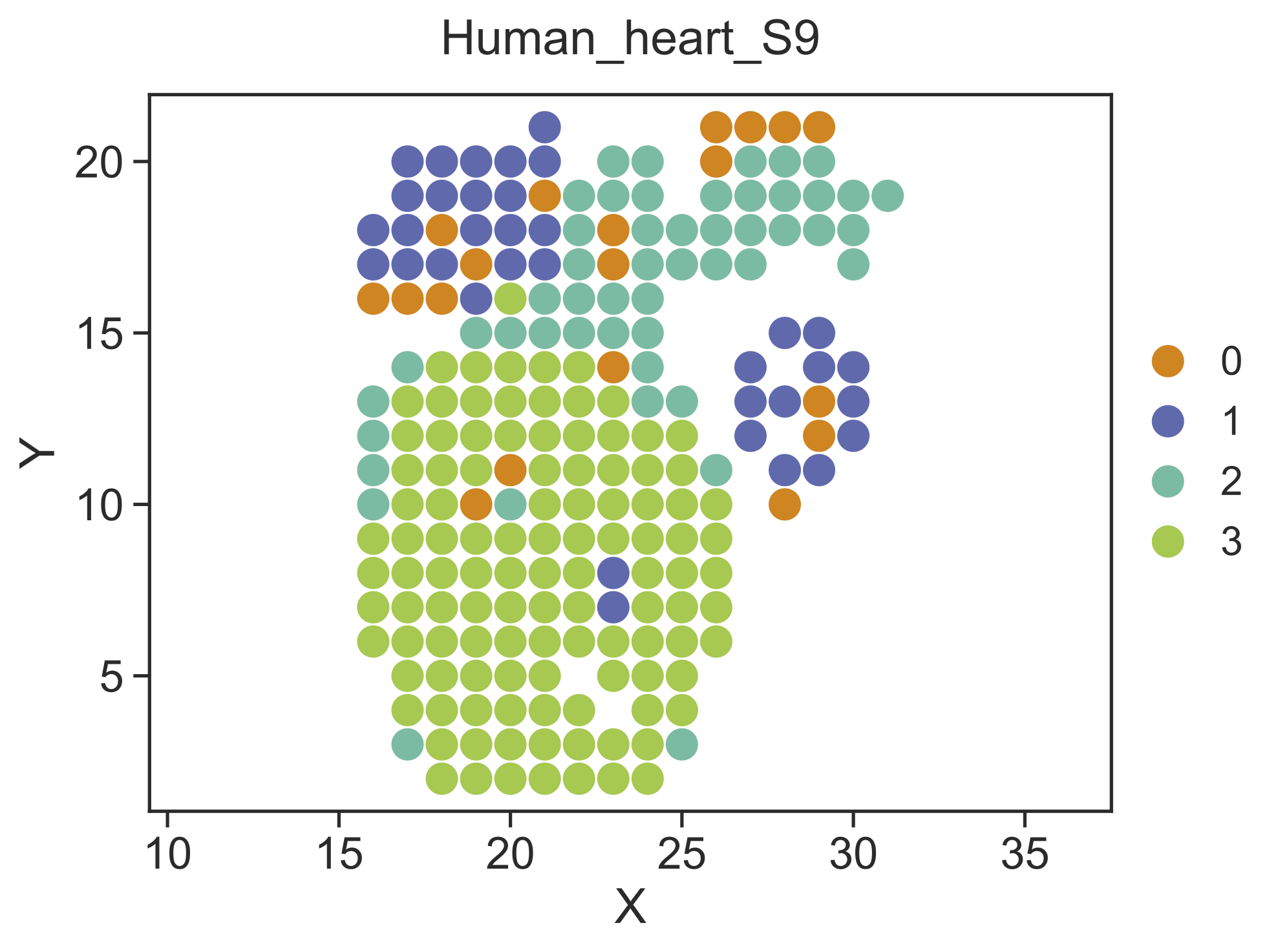
Step 3 Identify spatial domains¶
STRIDE could further identify the spatial domains by combining both the neighborhood information and the cell-type deconvolution result. Locations with similar cell-type compositions and similar surrounding cell populations will be clustered together. Also, users should specify the sample which they want to perform spatial clustering on.
STRIDE cluster --deconv-file Result/STRIDE/Human_heart_spot_celltype_frac.txt \
--st-loc Data/Human_heart_ST_location.txt --sample-id 9 \
--plot --pt-size 11 \
--weight 0.5 --ncluster 4 \
--outdir Result/STRIDE --outprefix Human_heart_S9
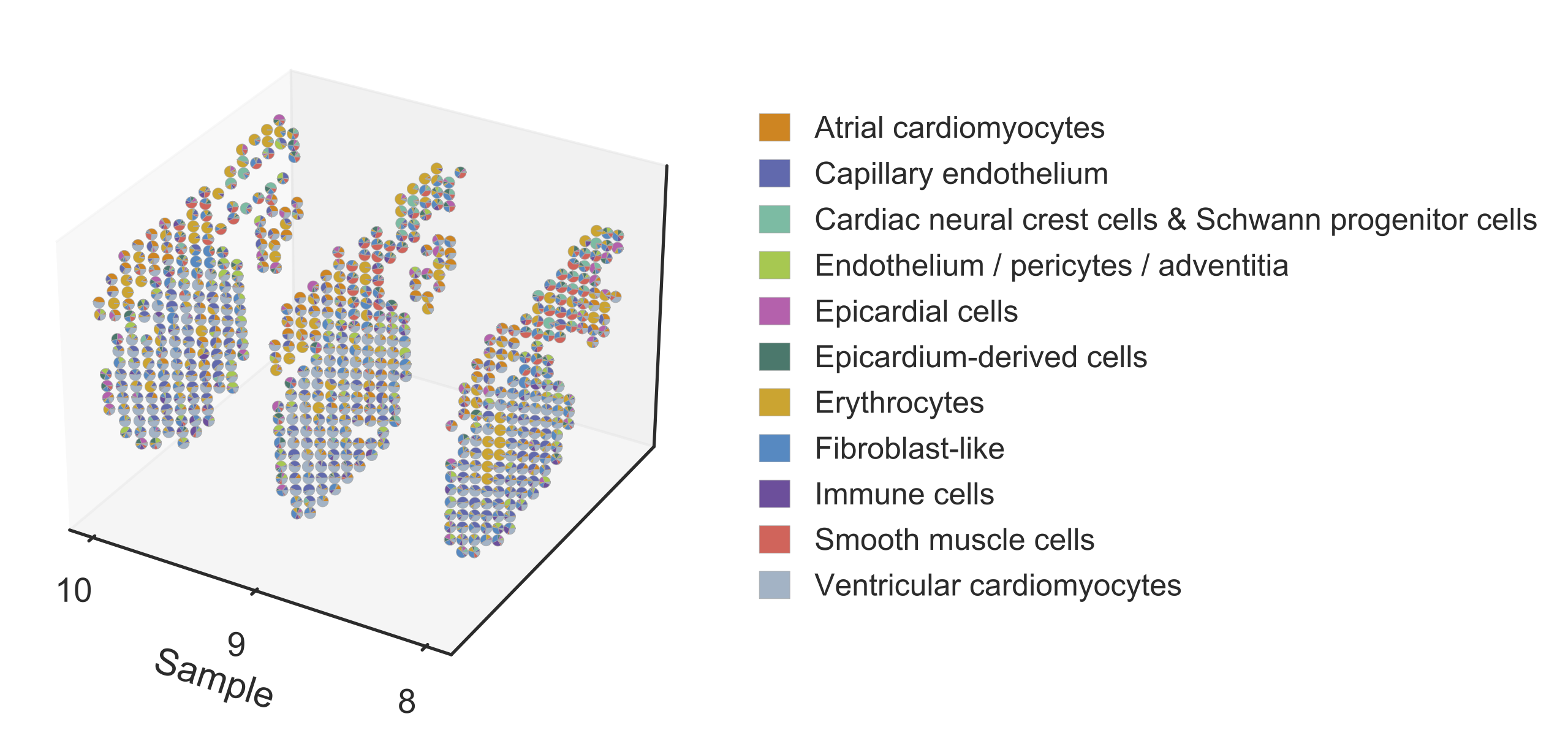
Step 4 Reconstruct the three-dimensional model of the human heart by slide integration¶
The original study provided multiple sequential slides at each timepoint, which we could use to reconstruct the three-dimensional model of the human heart. Here we take three sections from the 6.5 PCW heart, sample 8, 9, and 10, as an example to show the usage.
STRIDE integrate --deconv-file Result/STRIDE/Human_heart_spot_celltype_frac.txt \
--sample-id 8 9 10 --topic-file Result/STRIDE/Human_heart_topic_spot_mat_26.txt \
--st-loc Data/Human_heart_ST_location.txt \
--plot --pt-size 4.5 \
--outdir Result/STRIDE --outprefix Human_heart_6.5PCW